Open Source Legislation
US legislation scraped, normalized, and loaded into a unified knowledge graph. 44+ jurisdictions, open source.
US legislation is a mess. Every state has its own legal code, published on its own website, in its own format. If you want to research how different states handle the same issue (say, data privacy or employment law), you have to visit dozens of different websites and figure out each one's search interface.
I decided to fix this. Starting in 2023 as part of Recodify (the legal tech startup I co-founded), I built scrapers across US states and federal corpora, normalized everything into a consistent structure, and loaded it into a unified searchable database. When Recodify shut down in 2024, I open-sourced the whole thing. It's now at 44+ jurisdictions and still active.
The scraping challenge
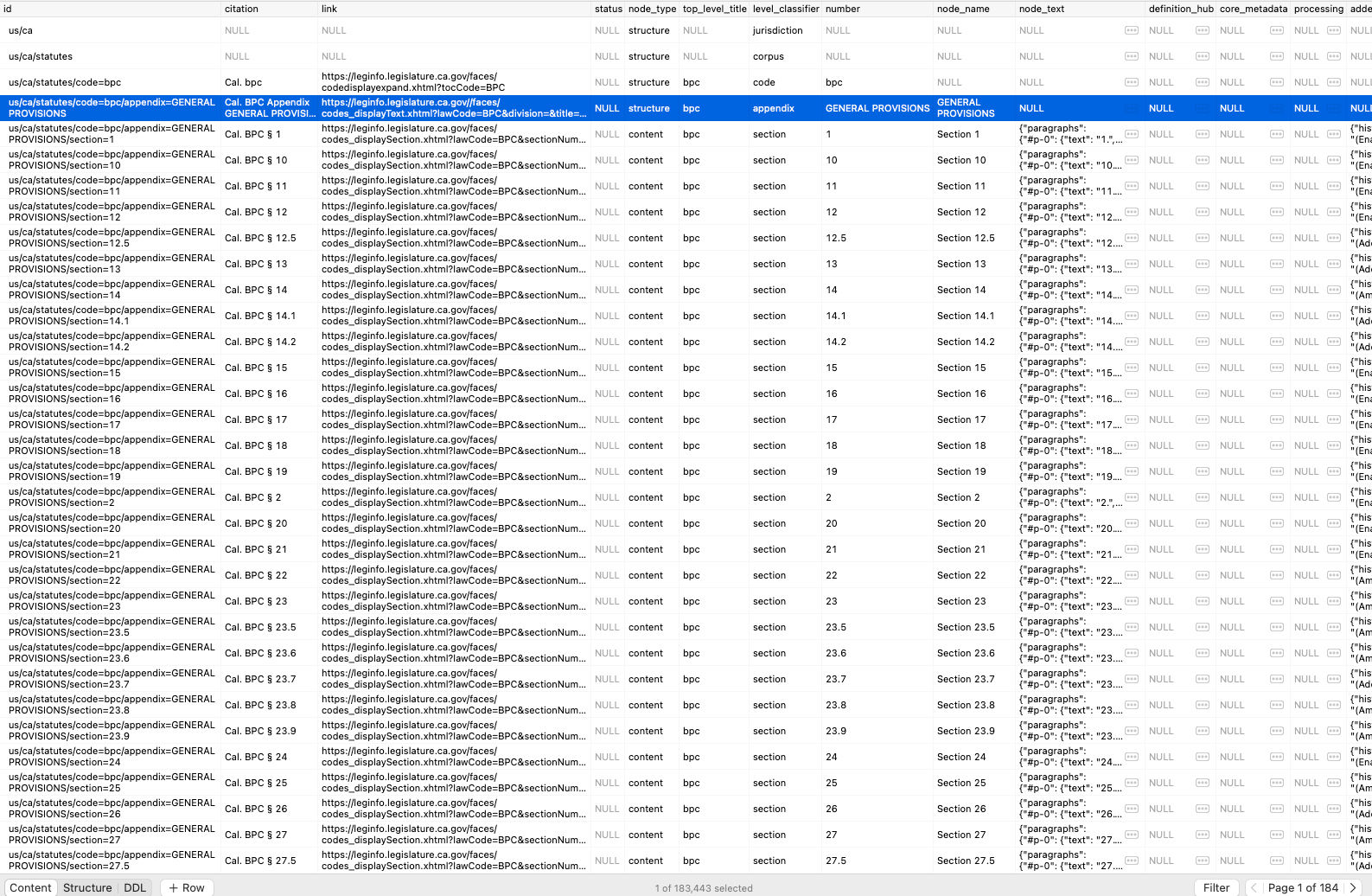
Every jurisdiction is different. Some publish their laws in clean XML. Some use HTML that looks like it was designed in 1998. Some are PDFs. California has over 150,000 sections. Wyoming has a few thousand. The hierarchy varies (some states have titles, chapters, sections, and subsections; others skip levels or use different naming).
Each scraper handles the quirks of its jurisdiction's website: rate limiting, session handling, pagination, malformed HTML. When a state updates their website (which happens more than you'd think), the scraper breaks and needs fixing. I built a standardized BaseScraper framework so new jurisdictions inherit all the infrastructure; only the HTML parsing logic is jurisdiction-specific.
Legislation as a knowledge graph
Once you have the data, the interesting problem is structure. Legislation isn't just a flat collection of text. It's a hierarchy (title, subtitle, part, section, subsection) with cross-references that cut across that hierarchy in ways that aren't always explicit in the text.
I modeled each legal code as a knowledge graph: the explicit tree structure as the foundation, plus extracted cross-references added as graph edges. A reference to "Title 5, Section 12" buried in a footnote becomes a traversable connection between two nodes. The graph captures legal relatedness that keyword search can't.
Definitions add another layer of complexity. Legal definitions only apply within specific subtrees: a term defined in "Title 5, Part 2" only has that meaning within Part 2, not globally. I built a definition scope system that processes all definitions, constructs "definition hubs" at the right parent level, and lets any query traverse to root to collect all definitions in scope.
What you can do with it
Once you have all the data in one place, interesting things become possible. You can compare how different states define the same term. You can find all the states that have laws about a specific topic. You can trace how legislation spreads: when one state passes a law, which states follow with similar language?
The search is semantic, not just keyword-based. Ask about "employee privacy rights" and you'll find relevant sections even if they don't use those exact words. Ask about "data breach notification requirements" and you get results from states that call it "security incident disclosure" or "consumer notification obligations."
A proto-agent before agents were a thing
The search interface works with keyword and semantic search. But I wanted something better: a system where you could ask a complex legal question and the AI would navigate the graph to find the answer, following cross-references and scoping to the right definitions as it went.
I built this in 2023, before "AI agents" was a common term. The pattern: embedding search gets you into the neighborhood of relevant legislation. Then you give the LLM tools to navigate the knowledge graph (traverse the hierarchy, follow cross-references, look up scoped definitions) and let it find the actual answer. Environment, structured data, traversable tools, and a goal. That's an agent. I was building one before I had a word for it.
Why open source
Laws should be accessible. The data is public (it's literally the rules we all have to follow) but it's been locked up in 50 different silos. By making this project open source, anyone can use it: researchers, journalists, legal aid organizations, civic tech projects.
The code is on GitHub. The database schema is documented. If you want to add a feature, fix a bug, or build something on top of it, you can.